In the previous post, AWS Config was introduced. We talked about how it can be used to obtain continuous compliance with your AWS account. In this post, we’ll implement a working example solution.
The typical architecture with AWS Config Rules looks like this:
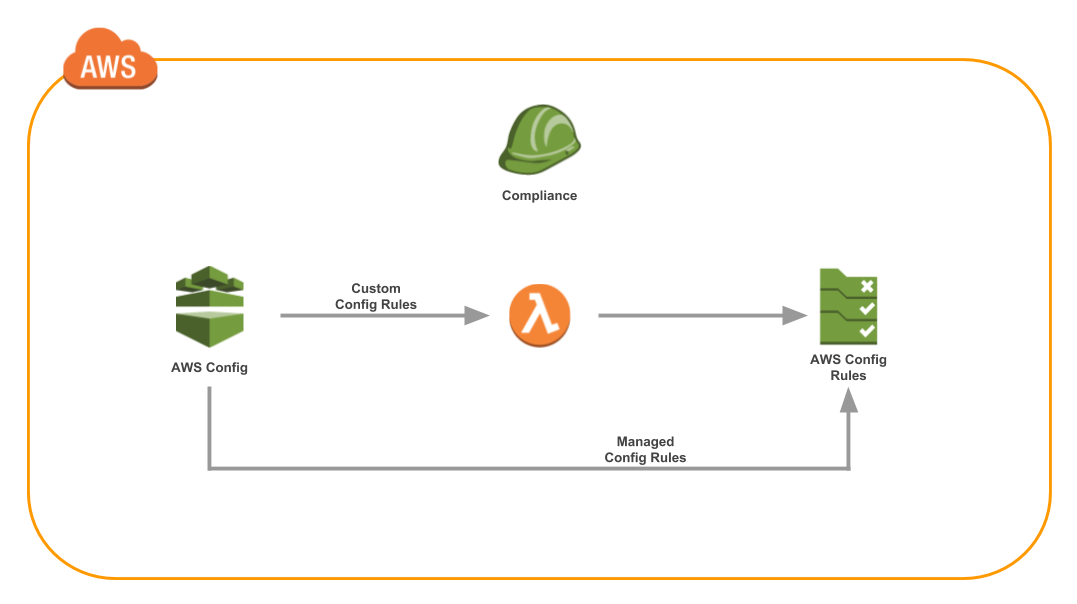
Typical CloudFormation Implementation
To create AWS Config Rules, the typical approach is to codify your infrastructure with CloudFormation. If you’re new to CloudFormation, check out the Introduction to CloudFormation series. CloudFormation is one of the most powerful tools from AWS. CloudFormation allows you to create any AWS resource with simple YAML.
Let’s take a look at some Config Rules implemented in CloudFormation. It looks something like this:
Resources:
CloudTrailLogIntegrityLambdaFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Code:
ZipFile: |
# ...
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# ...
config.put_evaluations(
Evaluations = evaluations,
ResultToken = result_token
)
Role: !GetAtt IamRole.Arn
Timeout: 20
MemorySize: 1536
FunctionName: rules-example-check_rule-cloud_trail_log_integrity
Handler: index.lambda_handler
Runtime: python3.6
CloudTrailLogIntegrityConfigRule:
Type: AWS::Config::ConfigRule
Properties:
ConfigRuleName: rules-example-check-cloud-trail-log-integrity
Source:
Owner: CUSTOM_LAMBDA
SourceIdentifier: !GetAtt CloudTrailLogIntegrityLambdaFunction.Arn
SourceDetails:
- EventSource: aws.config
MessageType: ConfigurationItemChangeNotification
- EventSource: aws.config
MessageType: OversizedConfigurationItemChangeNotification
Description:
CIS 2.2, 2.7 - Ensure CloudTrail log file validation is enabled
(Scored), ensure CloudTrail logs are encrypted at rest using KMS CMKs (Scored)
Scope:
ComplianceResourceTypes:
- AWS::CloudTrail::Trail
DependsOn: CloudTrailLogIntegrityPermission
CloudTrailLogIntegrityPermission:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Permission
Properties:
FunctionName: !GetAtt CloudTrailLogIntegrityLambdaFunction.Arn
Action: lambda:InvokeFunction
Principal: config.amazonaws.com
IncomingSshDisabledConfigRule:
Type: AWS::Config::ConfigRule
Properties:
ConfigRuleName: rules-example-check-incoming-ssh-disabled
Source:
Owner: AWS
SourceIdentifier: INCOMING_SSH_DISABLED
Description:
"CIS 4.1: Ensure no security groups allow ingress from 0.0.0.0/0
to port 22"
Scope:
ComplianceResourceTypes:
- AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
The full source code for this example project is at: tongueroo/config-rules-cloudformation. The command to launch the CloudFormation stack from the README is provided here for your convenience:
aws cloudformation create-stack --template-body file://config-rules.yml --stack-name config-rules --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM
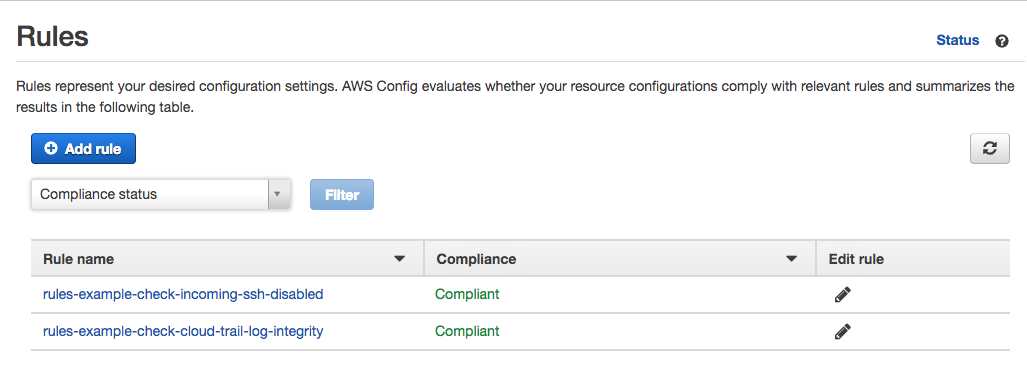
A few minutes after running the command, you’ll end up with 2 config rules:
- Managed Config Rule: Restrict Incoming SSH
- Custom Config Rule: Check CloudTrail Log Integrity
The Config Console should look something like this:
While the pure CloudFormation approach works, it can be improved.
Jets Serverless Framework Implementation
CloudFormation is described as “Infrastructure as Code.” Most programmers would not say that YAML is code though. YAML is really more like configuration. So in the above example, we are not really writing “Infrastructure as Code” but “Infrastructure as Configuration.”
With the Jets Serverless Framework we can truly write our the Config Rules as code. Here’s an example of how we would create the same Config Rules with Jets:
app/rules/check_rule.rb:
class CheckRule < ApplicationRule
class_runtime "python2.7"
desc "CIS 4.1 - Ensure no security groups allow ingress from 0.0.0.0/0 to port 22"
scope "AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup"
managed_rule :incoming_ssh_disabled
desc "CIS 1.3 - Ensure credentials unused for 90 days or greater are disabled"
scope "AWS::IAM::User"
python :rotate_user_passwords
end
The code takes advantage of Jets Polymorphic support. It defines a Python Lambda function and neatly organize it in separate file. The source code is here python/rotate_user_passwords.py
With only those few lines of code, the entire CloudFormation implementation has been replaced. Except, in this case, we have access to a programming language, not just YAML constructs. This is “Infrastructure as Code.”
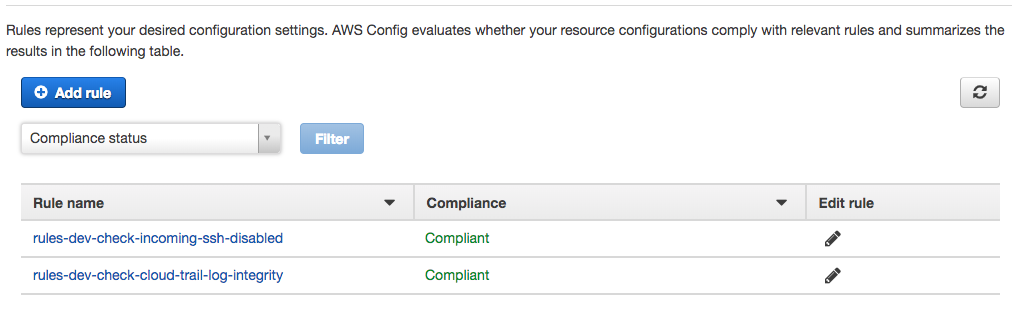
The AWS Config console looks something like this:
To deploy the application, it’s simple command:
jets deploy
Once you have access to the full power of a coding language, it becomes easier to add additional business logic like Daily Compliance Emails, Threshold Alarms, etc. You don’t have to write your code in one monolithic CloudFormation template.
Pricing
Note, running AWS Config Rules cost money and is not structured the same way you might be accustomed to. With EC2 pricing, you pay for usage on a per second basis. Once you turn off the instance, you stop paying.
With Config Rules, you pay $2/mo for each Config Rule once it reports compliance status for the very first time. Even if you destroy the Config Rule an hour later, you’ll still pay the $2 for that month. Pointing this out, so you are aware of it. This is why it is also nice that these example projects only have 2 rules to demonstrate working solutions without costing too much.
When you get to a higher number of rules, the pricing drops down to $1.50/mo/rule and then $1/mo/rule. You also pay $0.003 per configuration item recorded which can add up if you’re configuration changes often.
For more current prices refer to the AWS Config Rules Pricing.
Final Thoughts
In this post, we covered 2 ways to create AWS Config Rules:
- CloudFormation Raw Implementation
- Jets Framework Implementation
It’s interesting to note that ultimately Jets translates the code to CloudFormation anyway. A crude analogy is that we use compilers to convert a high-level programming language to machine code. Similarly, Jets translates the code to YAML. Additionally, Jets allows you access to more powerful programming language abilities that we’re accustomed to having.
It might not seem like there’s that not much that difference with only 2 AWS Config rules here. However, imagine having 10 or 20 Config Rules. We’re talking about 3 lines of code over the 20+ lines of YAML for each Config Rule here. The CloudFormation template gets pretty complicated quickly and leads to a ton of duplication. Coding with a tool like Jets that wraps CloudFormation makes for a cleaner and more maintainable experience.
Source code for both implementations are both on GitHub:



