In this post, we’ll cover the Terraspace 2.0 release. Here’s a summary:
- Terraspace Cloud Support
- New Concepts: TS_APP TS_ROLE TS_EXTRA
- Layering Improvements
- CI/CD Integration
Terraspace Cloud Support
First, what is Terraspace Cloud?
Terraspace Cloud is a nice addition to Terraspace. Terraspace Cloud adds extra features and conveniences to the Terraspace Framework like Team Management, Permissions, History, and a GUI visual interface. It’s specifically designed it work with Terraspace. Terraspace Cloud provides these additional conveniences as an optional paid managed service. It also hopefully provides a means to support the project financially. The Terraform Framework itself is open source and free to use. You can start using Terraspace Cloud with the Terraspace Framework starting in version 2.0.
New Concepts: TS_APP TS_ROLE TS_EXTRA
Version 2 introduces TS_APP TS_ROLE TS_EXTRA variables. These variables are like TS_ENV in that it allows you to generate a different permutation of a terraform project from a terraspace stack and deploy it. These variables are based on real-world experience, what I have used myself, and what I’ve seen other folks using.
The TS_APP allow you to deploy stacks that are scoped to apps. This is particularly useful for Azure, where a it’s common pattern uses resource groups to isolate and contain resources for a specific app. The new terraspace_plugin_azure generated resource group default is
terraform {
backend "azurerm" {
resource_group_name = "<%= expansion(':APP-:ENV-:LOCATION') %>"
...
With this major bump, Terraspace changed the defaults to better suite these new env vars. If your Terraspace project was originally generated with v1, then those initially generated backend keys remain the same. By design, you have to update those values manually.
The TS_ROLE env var was added as a part of this upgrade because I found it useful for some BoltOps project work. For example, a codebuild project can have the same app but different roles like: deploy or tests.
The TS_EXTRA is just a way to deploy an extra instance of the same stack. It replaces the --instance option. The --instance is now deprecated and will be removed in a future Terraspace version.
The nice thing about these new TS variables is that layering accounts for them. You can have app, role, or extra specific layers. Docs:
Layering Improvements
Layering has been improved with a focus on making them easier to debug. Layering has different modes with “simple” mode as the default. Essentially, the provider layer is no longer included by default. The new default is config.layering.mode = "simple". If you need the old v1 behavior, you can set config.layering.mode = "provider".
Layering now also accounts for App, Role, Extra level layering. Docs:
App and Role Layering Extra Layering
This most helpful tip and maybe my favorite improvement for layering is being able to see layerings by turning on config.layering.show
config/app.rb
Terraspace.configure do |config|
config.layering.show = true
end
This is extremely useful as it helps you immediately see what layers will be used.
CI/CD Integration
As a part of Terraspace Cloud support, CI/CD Integration has been added. Docs:
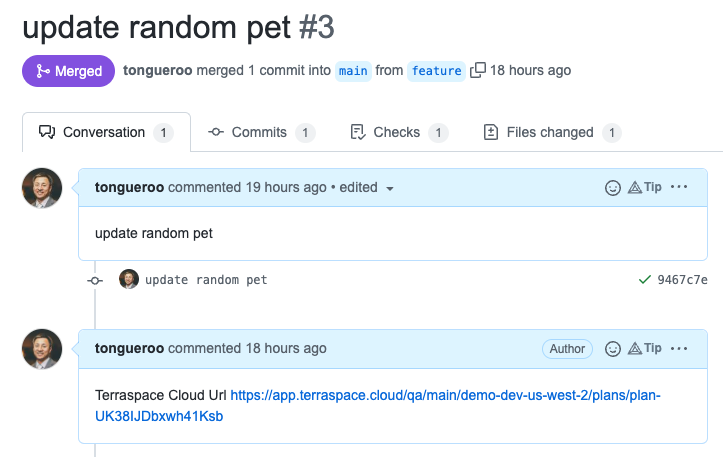
The CI plugins automatically pull in info like commit sha, branch name, and PR info from the CI environment. These get sent to Terrraspace Cloud and recorded to provide historical tracking information. For the GitLab and GitHub plugins, a PR comment is also added with a link to the Terraspace Cloud plan or update.
Summary
It’s been pretty cool to see the Terraspace Community continue to grow. Have learned a lot from seeing how others are using Terraspace and a decent amount of these updates are based on those learnings. Hopefully, you’ll enjoy these Terraspace upgrades. 🥂



